Distinguishing between sacroiliac pain and piriformis syndrome is essential in accurately diagnosing and treating lower back and buttock discomfort. While the symptoms of both conditions may overlap, their underlying causes and treatment approaches differ significantly. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of sacroiliac pain and piriformis syndrome while offering guidance on how to identify the source of your pain. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
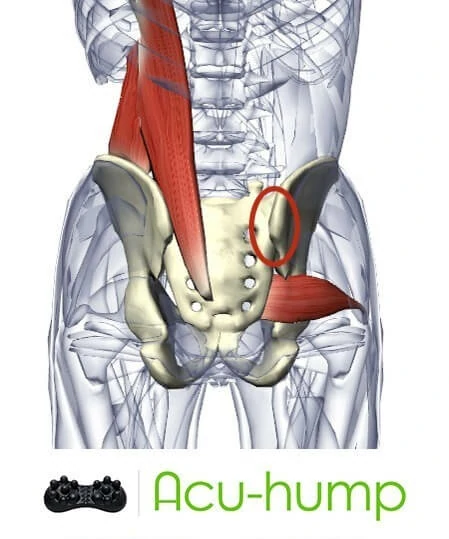
What is Sacroiliac Pain
Definition and Causes
Sacroiliac pain refers to discomfort originating from the sacroiliac joint, which connects the sacrum bone in your lower spine to the pelvis. Several factors can contribute to sacroiliac pain, including injury, inflammation, pregnancy, or degenerative conditions such as arthritis. Understanding these causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Identifying Symptoms
Symptoms associated with sacroiliac pain often manifest as lower back pain that radiates to the buttocks or thighs. It may be sharp or dull and is commonly localized around the sacroiliac joint area. Patients might experience difficulty standing, sitting, or changing positions without discomfort. Additionally, instability or a sensation of the back or pelvis “giving way” might be present.
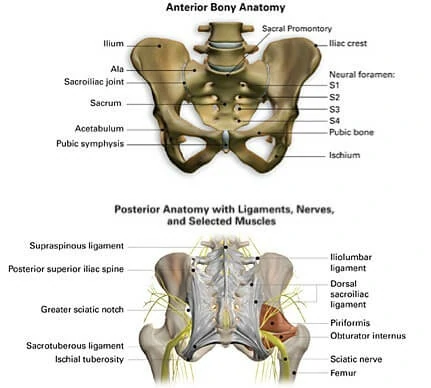
Diagnostic Techniques
Diagnosing sacroiliac pain requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. They may employ various diagnostic techniques to determine the source of your discomfort, including:
Physical examination
The healthcare professional will assess your range of motion, joint stability, and tenderness around the sacroiliac joint. They may perform specific orthopedic tests to elicit pain or reproduce symptoms.
Imaging tests
X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be ordered to obtain detailed images of the sacroiliac joint and surrounding structures. These tests can help identify any structural abnormalities or signs of inflammation.
Diagnostic injections
In some cases, diagnostic injections may be used to confirm the diagnosis of sacroiliac pain. A numbing medication is injected into the sacroiliac joint, providing temporary relief from pain. If the pain subsides significantly after the injection, it suggests that the sacroiliac joint is the source of the discomfort.
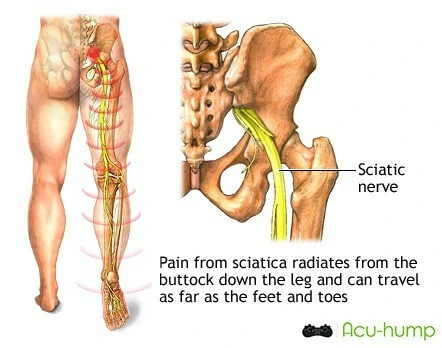
What is Piriformis Syndrome
Definition and Causes
Piriformis syndrome is a condition characterized by the compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle located deep in the buttock. The causes of piriformis syndrome can result from muscle tightness, overuse, trauma, or anatomical variations.
Identifying Symptoms
The symptoms of piriformis syndrome can be quite similar to those of sacroiliac pain, making it challenging to differentiate between the two conditions. However, there are specific symptoms that can help identify piriformis syndrome, including:
- Deep buttock pain: Patients often experience pain deep within the buttock, on one side or both sides.
- Radiating pain: The pain may radiate down the back of the thigh and even into the calf or foot, following the path of the sciatic nerve.
- Aggravated by sitting: Sitting for prolonged periods or engaging in activities that apply pressure on the piriformis muscle, such as running or climbing stairs, can worsen the pain.
- Muscle tightness or spasms: Patients may report tightness or spasms in the buttock region, particularly when walking or exercising.
- Tingling or numbness: Some individuals may experience sensations of tingling, numbness, or even weakness in the affected leg.

Acu-hump®
Deep Massage Hip & Butt
Diagnostic Techniques
Imaging tests: Similar to sacroiliac pain, imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be ordered to rule out other potential causes of your symptoms. These tests can help visualize the piriformis muscle and identify any structural abnormalities or signs of inflammation.
Electromyography (EMG): In some cases, an EMG may be performed to assess the function of the sciatic nerve and determine if it is being compressed or affected by the piriformis muscle.
Diagnostic injections: Another diagnostic technique used for piriformis syndrome is a diagnostic injection of a local anesthetic directly into the piriformis muscle. If the pain significantly diminishes or resolves after the injection, it suggests that piriformis syndrome is the likely cause of your symptoms.
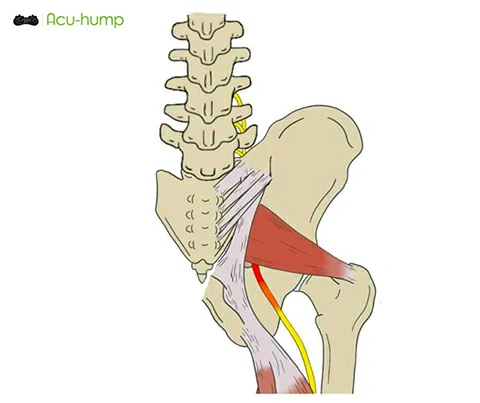
Differentiating between sacroiliac pain and piriformis syndrome
Differentiating between sacroiliac pain and piriformis syndrome can be challenging due to their overlapping symptoms. However, there are certain characteristics that can help distinguish between the two conditions:
Location of Pain
Sacroiliac pain typically manifests as lower back pain that radiates to the buttocks or thighs. The discomfort is often localized around the sacroiliac joint area. In contrast, piriformis syndrome is characterized by deep buttock pain that can radiate down the back of the thigh, following the path of the sciatic nerve.
Aggravating Factors
Both conditions may be aggravated by certain activities, but there are differences. Sacroiliac pain may worsen with weight-bearing activities such as standing, walking, or changing positions. On the other hand, piriformis syndrome is often exacerbated by sitting for prolonged periods or engaging in activities that put pressure on the piriformis muscle, such as running or climbing stairs.
Associated Symptoms
Individuals with sacroiliac pain may experience instability or a sensation of the back or pelvis “giving way.” On the other hand, piriformis syndrome may be accompanied by muscle tightness or spasms in the buttock region, as well as tingling, numbness, or weakness in the affected leg.
Response to Treatment
Sacroiliac pain may respond well to physical therapy, stabilization exercises, and specific sacroiliac joint mobilization techniques. On the other hand, piriformis syndrome may show improvement with targeted stretching and strengthening exercises for the piriformis muscle, along with techniques to release any muscle tension or tightness.
Diagnostic Techniques
Diagnostic techniques, such as physical examination, imaging tests, and diagnostic injections, can also help differentiate between the two conditions. Physical examination can reveal tenderness and specific movement patterns that elicit pain in the sacroiliac joint or piriformis muscle. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, can provide visual confirmation of structural abnormalities or signs of inflammation. Diagnostic injections, such as numbing medication injected into the sacroiliac joint or piriformis muscle, can help determine if the pain originates from those specific areas.

Acu-hump: 30-day return policy.
You have no risk.
Distinguishing between sacroiliac pain and piriformis syndrome is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment approach for your lower back and buttock discomfort. While both conditions can present with similar symptoms, understanding the specific characteristics and utilizing diagnostic techniques can help healthcare professionals accurately identify the source of your pain. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional is vital to obtain an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for your condition.
Acu-hump® Massage & Stretch the Butt and Back
